Dynamic range compression
 Dynamic range compression (DRC) or simply compression reduces the volume of loud sounds or amplifies quiet sounds by narrowing or "compressing" an audio signal's dynamic range. Compression is commonly used in sound recording and reproduction and broadcasting.
Dynamic range compression (DRC) or simply compression reduces the volume of loud sounds or amplifies quiet sounds by narrowing or "compressing" an audio signal's dynamic range. Compression is commonly used in sound recording and reproduction and broadcasting.
Audio compression reduces loud sounds which are above a certain threshold while quiet sounds remain unaffected. The dedicated electronic hardware unit or audio software used to apply compression is called a compressor. In recorded and live music, compression parameters may be adjusted by an audio engineer to change the way the effect sounds.

Downward compression Upward compression
Types
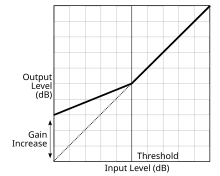
Downward compression reduces loud sounds over a certain threshold while quiet sounds remain unaffected. Upward compression increases the loudness of sounds below a threshold while leaving louder passages unchanged. Both downward and upward compression reduce the dynamic range of an audio signal.
An expander performs the opposite function, increasing the dynamic range of the audio signal. Expanders are generally used to make quiet sounds even quieter by reducing the level of an audio signal hat falls below a set threshold level. One example of an expander is a noise gate.
No comments:
Post a Comment